Researchers Develop Human Cell-Based Model to Study Small Cell Lung Cancer
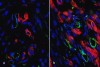
New York, NY, USA – Researchers from Weill Cornell Medicine have used human embryonic stem cells to create a new model system that allows them to study the initiation and progression of small cell lung cancer (SCLC). The study, which will be published February 8 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, reveals the distinct roles played by two critical tumor suppressor genes that are commonly mutated in these highly lethal cancers.